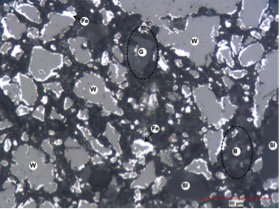
A fluidized bed reactor in a smelting reduction process represents a high sophisticated technology which enables operators to adapt to different requirements. It is possible to reduce fine iron ores without the energy-intensive process of sintering. The aim of this study is to determine the of ultra fine iron ore (< 63 µm) on a circulating fluidized bed in a cold testing model. Moreover, various binding concepts for a production of micro pellets are evaluated concerning their suitability for processing in a fluidized bed reactor. Fig. 1 shows a microsection of a reduced pellet which matches the critical parameters of reducibility and compressive strength.