Project Title:
Characterisation of non-metallic inclusions in Ti-stabilised ferritic stainless steels
Industrial Partner:
Project Description:
In the group of stainless steels austenitic steels are the most important ones. But due to the often fluctuating nickel price, Ti-alloyed ferritic stainless steels are seen as a competitive alternative, because they offer similar mechanical and corrosion properties. Hence Titanium alloyed ferritic stainless steels are getting more and more important in recent years.
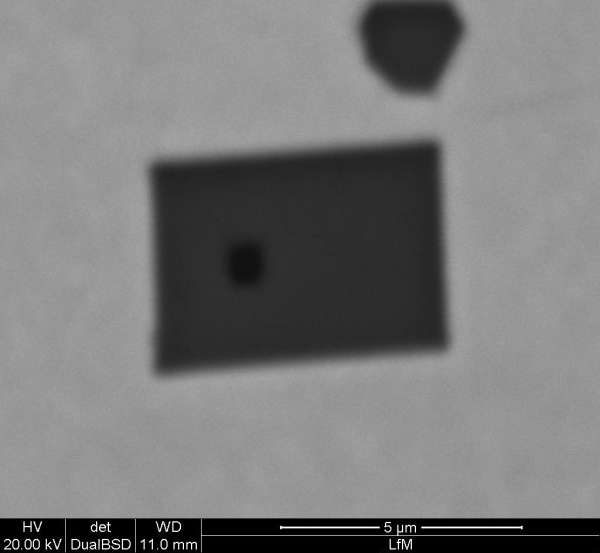
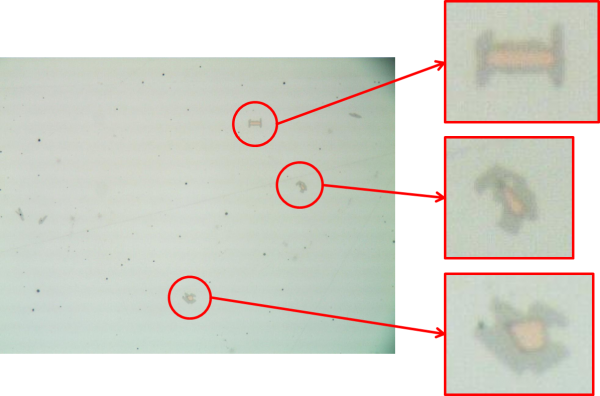
However alloying of Titanium can change the inclusion landscape: The added Titanium forms TiN, TiC and Ti(C,N), which interact with other endogenous or exogenous (slag entrapments or refractories) inclusions. The resulting inclusions or inclusion clusters can lead to casting problems, like clogging, and surface defects in final products. For the improvement of castability and surface quality of Titanium alloyed ferritic steels it is important to analyse the inclusion landscape in these steel grades in order to get information about inclusion formation and modification. With this information a specific control and modification of the inclusion landscape is possible.
Figures:
References:
Park, J.H.: Thermodynamic investigation on the formation of inclusions containing MgAl2O4 spinel during 16Cr–14Ni austenitic stainless steel manufacturing processes, Materials Science and Engineering A 472 (2008), 43-51.
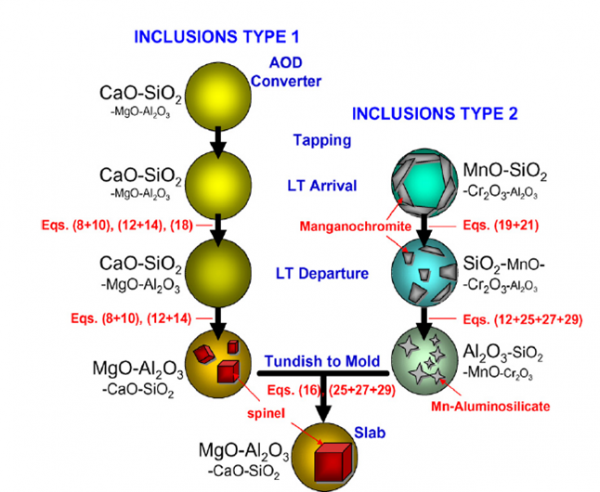
Schematic illustration of the inclusion formation mechanism during stainless steel production process